Process 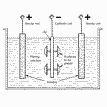
| Electrodeposited coatings (plating) Electrodeposition is used for
applying metal coatings for decoration or corrosion resistance. It is
suitable for thin coatings because slow and costly (for thick coatings
not cost effective). The process is carried out in an electrolytic cell.
The cell contains a liquid (electrolyte, electrical conductor), a
solution in water of the metal to be deposited. The negative electrode
(cathode) is the part to be coated, the positive (anode) is the coating
metal. Multiple layers systems also applied.
Under low voltage current, the electrolytes move towards the
cathode and deposit on it. Coating's thickness dependent on the
intensity of current; not uniform for irregular shapes and blind holes;
hydrogen embrittlement problems.
|
Danish Name | Elektrolytisk udfældning |
Category | Surface coatings
|
Materials | Coating materials:, Pure metals (Zn, Ni, Cu, Sn) , Alloys, Precious metals |
References | Arbeitsgemeinschaft der Deutschen Galvanotechnik, (Germany)
|
Environmental
notes | Old types of electrodeposition plants can have pollution problems |
